In the changing business landscape of the UAE, understanding the importance of corporate taxation is essential for both local companies and international companies operating within its borders. With a tax system known for its business-friendly environment, understanding how corporate tax is calculated in the UAE is essential. Unlike many other jurisdictions, the UAE does not impose a federal corporate income tax on most businesses. Instead, the country operates under a system where corporate tax (CT) is administered primarily at the emirate level. Each emirate has its own rules and policies regarding taxation.
CT in the UAE is calculated at 9% of the net profit shown in the company’s financial statements, after deducting all applicable deductions and excluding exempt income. Any foreign tax paid is allowed to be deducted from the profit shown in the financial statement.
Let’s examine the method of how corporate tax is calculated in the UAE using the table provided below.
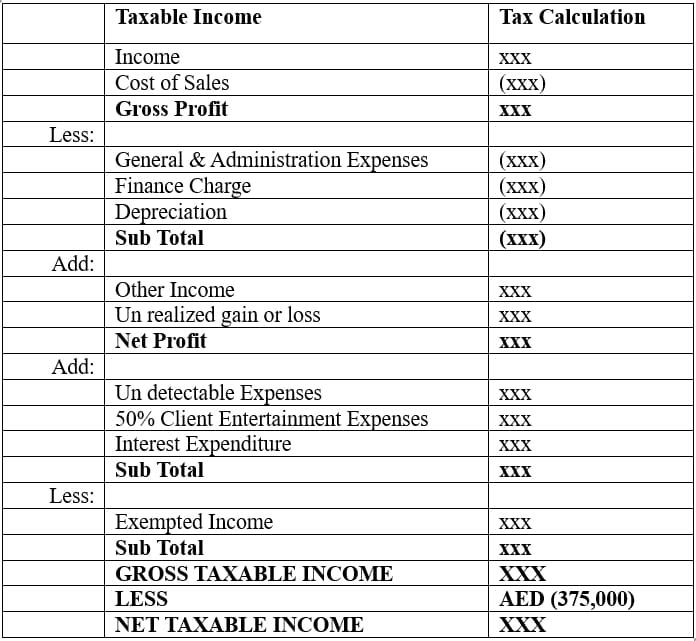
Gross Amount of any sales or services derived by a Taxable person during a Tax Period
The following income and related expenditure shall not be taken into account in determining the Taxable Income
All legitimate business expenses incurred wholly and exclusively for the purposes of deriving Taxable Income will be deductible including purchases, Labor Charges, Hire Charges, Sub Contractors etc., Expenditure related to the exempted income should not be part of cost of sale.
A Taxable Person that prepares financial statements on an accrual basis can depreciate / Amortize under applicable accounting standards for its property, plant and equipment, investment property, intangible assets or other non-current assets.
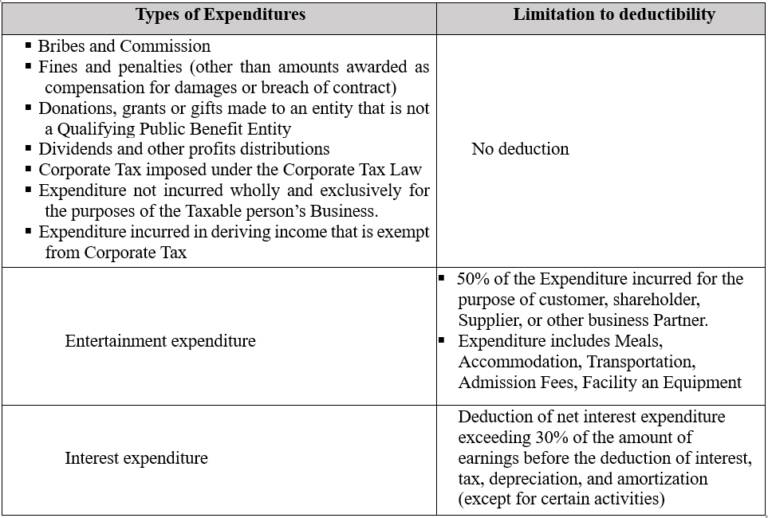
Certain expenses which are deductible under general accounting rules may not be fully deductible for CT purposes. These will need to be added back to the Accounting Income for the purposes of determining the Taxable Income. Examples of expenditure that is or may not be deductible (partially or in full) include:
Maxims offers complete assistance with corporate tax registration, filing, payments and ongoing support in the UAE. Our dedicated team of tax experts, well versed in UAE tax laws, ensure smooth and legal business transactions. We also offer customized consulting services to address specific tax concerns or challenges faced by businesses. During a tax audit or investigation, we stand by our clients, providing support and representation throughout the process.